Have you ever wondered how birds are able to soar through the sky with such grace and agility? Well, prepare to be amazed as we dive into the fascinating world of bird respiration.
In this article, we will explore the intricate structure of bird lungs and unravel the secrets behind their efficient oxygen exchange system.
From adaptations for high altitude flights to the seamless connection between vocalization and respiration, birds have truly evolved to master the art of breathing.
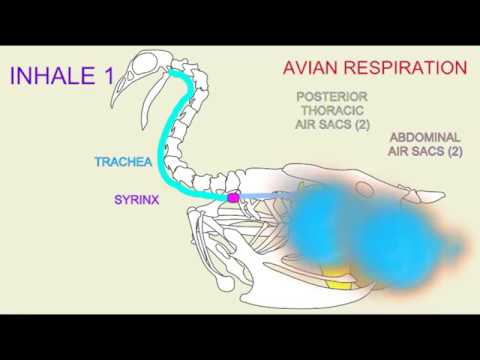
Related Video: "avian respiration" by Walter Jahn
However, it’s not all smooth flying for our feathered friends, as they face unique respiratory challenges that set them apart from other creatures.
So, get ready to embark on a scientific journey that will leave you with a newfound appreciation for the incredible respiratory system of birds. Let’s uncover the mysteries of avian respiration together!
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
– Pollution has a significant impact on the respiratory health of birds, leading to decreased lung capacity, increased susceptibility to respiratory infections, respiratory tissue damage, and impaired respiratory function.
– Respiratory diseases in birds can be caused by viral and bacterial infections, as well as environmental pollutants and habitat degradation, ranging from mild infections to severe respiratory distress and affecting overall health and survival of avian species.
– Human activities such as deforestation and urbanization disrupt bird habitats, leading to a decline in bird populations. Restoring bird habitats and providing necessary resources for the respiratory system are crucial for their well-being.
– Creating bird-friendly habitats by planting native trees and shrubs, providing bird feeders and water sources, creating nesting sites, minimizing outdoor cat presence, and avoiding excessive noise and disturbance can help support the respiratory health of birds.
The Structure of Bird Lungs
You might be surprised to learn that your feathered friends, birds, actually have a unique and intricate respiratory system that includes lungs specifically designed to maximize oxygen intake. Bird lung anatomy is quite different from that of mammals, with some fascinating respiratory adaptations.
Bird lungs are relatively small compared to their body size, but they are highly efficient. Instead of being large and spongy like mammalian lungs, bird lungs are compact and rigid. They are composed of multiple air sacs, which are connected to the lungs and extend throughout the bird’s body. These air sacs play a crucial role in the bird’s breathing process, as they act as a continuous flow-through system, allowing for a unidirectional flow of air.
This unique structure enables birds to have a constant supply of fresh oxygen-rich air during both inhalation and exhalation. As a result, birds have a higher oxygen exchange rate and can maintain a higher metabolic rate, which is essential for their active and energetic lifestyle. This respiratory system also helps birds tolerate high altitudes and fly at great speeds.
Now, let’s delve into the fascinating process of oxygen exchange in birds, where these specialized lungs play a crucial role in providing the necessary oxygen for their bodies to function optimally.
Oxygen Exchange in Birds
Experience the wonder of how oxygen is exchanged in the remarkable respiratory system of these avian creatures. Birds have a highly efficient system for oxygen transport, allowing them to thrive in their aerial environments. Here is a breakdown of the oxygen exchange process in birds:
1. Air enters the bird’s respiratory system through the trachea, which then splits into smaller tubes called bronchi, finally reaching the bronchioles.
2. The bronchioles lead to tiny air sacs called parabronchi, which are responsible for the actual gas exchange. These parabronchi have a unique structure, with a one-way flow of air that ensures maximum oxygen absorption.
3. As the air passes through the parabronchi, oxygen diffuses from the air sacs into the blood vessels surrounding them. Carbon dioxide, a waste product, simultaneously diffuses from the blood vessels into the air sacs to be exhaled.
4. The oxygen is then transported by the bird’s circulatory system to the body’s cells, where it is utilized for energy production.
The intricate lung structure and efficient oxygen exchange process of birds allow them to thrive in diverse environments.
Now, let’s explore the fascinating adaptations these incredible creatures have developed to survive at high altitudes.
Adaptations for High Altitude
When it comes to coping with low oxygen levels at high altitudes, birds have some impressive adaptations. Their specialized respiratory structures play a crucial role in enabling them to thrive in these challenging environments.
For example, some high-flying birds have larger lungs and air sacs, allowing for more efficient oxygen exchange. Additionally, they have a higher concentration of red blood cells and a unique cardiovascular system that helps deliver oxygen to their muscles more effectively.
How birds cope with low oxygen levels at high altitudes
Flying high above the clouds, you may wonder how birds manage to thrive in low oxygen environments at high altitudes. It’s fascinating to learn about the bird adaptations that allow them to cope with the effects of altitude. Here are five key mechanisms that enable birds to survive in these challenging conditions:
– Enhanced oxygen-carrying capacity of blood due to a higher concentration of red blood cells.
– Efficient use of oxygen by their muscles, which have a greater number of mitochondria.
– Increased lung ventilation to maximize oxygen intake.
– Ability to extract more oxygen from the air by having a higher number of capillaries in their lungs.
– Unique hemoglobin structure that has a higher affinity for oxygen, enabling efficient oxygen binding and release.
Understanding these adaptations helps us appreciate the intricate mechanisms that enable birds to thrive in low oxygen environments.
Transitioning to the subsequent section about the role of specialized respiratory structures in high-flying birds, it becomes clear how these adaptations are crucial for their survival.
The role of specialized respiratory structures in high-flying birds
High-flying birds rely on specialized respiratory structures to efficiently extract oxygen from the thin air at high altitudes. These birds have evolved unique breathing techniques and specialized adaptations to overcome the challenges posed by low oxygen levels.
One such adaptation is the presence of air sacs that extend into their bones, allowing for a continuous flow of oxygen-rich air throughout their bodies. In addition, their lungs are more efficient than those of other animals, with a higher surface area for gas exchange. This enables them to extract a greater amount of oxygen from each breath.
Furthermore, high-flying birds have a higher concentration of oxygen-carrying molecules, such as hemoglobin, in their blood. These adaptations allow them to thrive in environments where oxygen is scarce.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about birds that thrive in high-altitude environments, we can explore specific examples of these remarkable avian species.
Examples of birds that thrive in high-altitude environments
You’ll be amazed by the incredible high-altitude dwellers. These magnificent avian species have adapted to thrive in environments where oxygen is scarce. Here are three examples of high altitude bird species and their remarkable respiratory adaptations:
1. The Bar-headed Goose: This species is known for its ability to migrate over the Himalayas, reaching altitudes of up to 7,000 meters. It has enlarged lungs and specialized hemoglobin that allows it to extract oxygen efficiently from thin air.
2. The Andean Condor: Found in the Andes Mountains, this bird has a massive wingspan of up to 3 meters, allowing it to soar effortlessly at high altitudes. It has large air sacs connected to its lungs, which increase its respiratory efficiency.
3. The Snowy Owl: These owls inhabit the Arctic where oxygen levels are low. They have unique air sacs and a rigid respiratory system that prevents collapse during flight and enables them to hunt effectively in high-altitude environments.
Now, let’s explore how these high-altitude birds have developed unique vocalization and respiration mechanisms.
Vocalization and Respiration
To fully appreciate the intricate connection between vocalization and respiration, you must understand the remarkable lung capacity of birds. Vocalization techniques in birds rely heavily on their respiratory adaptations, which allow them to produce a wide range of sounds. Birds possess a unique vocal organ called the syrinx, located at the base of their trachea. Unlike mammals, where vocalization is primarily produced in the larynx, birds can generate sound from both the syrinx and the larynx simultaneously, enabling them to produce complex melodies and harmonies.
Birds have evolved specialized respiratory systems that support their vocalization capabilities. One key adaptation is the presence of air sacs, which act as reservoirs and aid in the efficient exchange of gases. These air sacs extend into various parts of their body, including the bones, which not only contribute to their lightweight structure but also enhance their lung capacity. Additionally, birds have a highly efficient gas exchange system, with unidirectional airflow through their lungs. This means that oxygen-rich air flows continuously through their lungs, ensuring an ample supply of oxygen for both vocalization and metabolism.
Understanding the relationship between vocalization and respiration in birds is crucial for comprehending their behavior, communication, and evolutionary adaptations. The remarkable lung capacity and respiratory adaptations of birds allow them to produce intricate and melodious songs, making them one of the most fascinating creatures in the animal kingdom.
As we delve into the next section on the respiratory challenges for birds, we will explore how these adaptations are put to the test in different environments and lifestyles.
Respiratory Challenges for Birds
When it comes to the respiratory challenges faced by birds, pollution can have a significant impact on their respiratory health. Birds are highly susceptible to air pollution, which can lead to respiratory diseases and respiratory distress.
As humans, we can play a crucial role in protecting bird respiratory systems by reducing pollution levels and creating cleaner environments for them to inhabit.
The impact of pollution on avian respiratory health
Imagine being a bird, soaring through the sky, but constantly battling the harmful effects of pollution on your delicate respiratory system. The impact of air pollution on avian respiratory health, especially in urban areas, is a topic of great concern. Here are four key ways in which pollution affects the respiratory health of birds:
1. Reduced lung capacity: Birds exposed to high levels of air pollution may experience a decrease in lung capacity, limiting their ability to take in oxygen efficiently.
2. Increased susceptibility to respiratory infections: Air pollution weakens the immune system of birds, making them more susceptible to respiratory infections and diseases.
3. Respiratory tissue damage: Toxic chemicals present in polluted air can cause damage to the respiratory tissues of birds, leading to inflammation and scarring.
4. Impaired respiratory function: Airborne pollutants can disrupt the normal functioning of the respiratory system in birds, leading to breathing difficulties and reduced oxygen intake.
As we delve deeper into the topic of respiratory diseases in birds, it becomes evident that pollution plays a significant role in compromising their respiratory health.
Respiratory diseases in birds
Take a moment to envision yourself as a majestic creature in the sky, burdened with the weight of respiratory diseases that afflict your fellow avian beings. The avian respiratory system, designed for the demanding task of flight, is susceptible to various respiratory health issues.
Birds have a unique respiratory system that allows for efficient oxygen uptake during flight. However, this complex system also exposes them to potential risks.
Respiratory diseases in birds can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral and bacterial infections, environmental pollutants, and habitat degradation. These diseases can range from mild infections to severe respiratory distress, affecting the overall health and survival of avian species.
By understanding and addressing the factors that contribute to respiratory diseases, we can take steps to protect and preserve the respiratory health of birds.
How humans can help protect bird respiratory systems
To help protect the respiratory health of our feathered friends, you can make a difference by creating bird-friendly habitats and reducing pollutants in their environment. Bird migration is a natural phenomenon that allows birds to travel long distances in search of food, breeding grounds, and suitable habitats. However, human activities such as deforestation and urbanization have disrupted these habitats, leading to a decline in bird populations. By restoring bird habitats, you can provide them with the necessary resources for their respiratory system to function properly. Additionally, reducing pollutants such as air pollution and pesticide use can greatly benefit birds’ respiratory health. Creating bird-friendly habitats and reducing pollutants are essential steps in ensuring the well-being of our avian companions.
| Key Actions for Bird-friendly Habitats | Key Actions for Reducing Pollutants |
|---|---|
| Plant native trees and shrubs | Limit the use of chemicals |
| Provide bird feeders and water sources | Use environmentally-friendly products |
| Create nesting sites | Reduce air pollution |
| Minimize outdoor cat presence | Properly dispose of waste |
| Avoid excessive noise and disturbance | Support renewable energy sources |
Frequently Asked Questions
How do birds obtain oxygen at high altitudes?
At high altitudes, birds face hypoxic conditions where oxygen is scarce. However, through their remarkable hypoxic adaptation, birds utilize air sacs to efficiently extract oxygen from the thin air, ensuring their survival in extreme environments.
Can birds breathe underwater like some aquatic animals?
No, birds cannot extract oxygen from water like aquatic animals. They do not have specialized respiratory adaptations for diving. Instead, birds rely on their lungs and air sacs to extract oxygen from the air.
Do birds have a diaphragm like mammals?
Birds have a diaphragm, similar to mammals, which aids in their respiration. However, their respiratory system differs from mammals in several key ways, including the presence of air sacs and the ability to extract oxygen more efficiently.
Can birds hold their breath for long periods of time?
Birds have a unique respiratory system that allows them to hold their breath for short periods of time. The air sacs in their bird lungs and avian respiration play a crucial role in this process.
Why do birds sing while they breathe?
Birdsong communication in birds is facilitated by respiratory adaptations. These adaptations allow them to produce complex vocalizations while maintaining a steady flow of air. These specialized mechanisms enable birds to sing while breathing.



